“503 Service Unavailable” Error on the vSphere Web Client: What Should You Do?
VMware vCenter Server, the centralized management point in vSphere, is used for managing ESXi hosts, clusters, VMs, and other components in your virtualized data center. This blog post addresses the 503 Service Unavailable that you may get in vSphere Client when you try to connect to vCenter. Read to learn about the potential causes of this error and how to fix it.
What is “503 service unavailable” error?
503 Service Unavailable is one of the standard HTTP status codes that are returned by a server when a client sends a request to the server. The 5xx class of HTTP status codes is used to notify users about server errors. Based on this, 503 Service Unavailable is a response that describes a server-side error. Usually this error indicates that a server cannot handle a request and you should look for the issue on the web server hosting an application.
Here’s the full text of this error for VMware vSphere Client:
503 Service Unavailable (Failed to connect to endpoint: [N7Vmacore4Http20NamedPipeServiceSpecE:0x000055615a4d7a70] _serverNamespace = / action = Allow _pipeName =/var/run/vmware/vpxd-webserver-pipe)
In the case of the vCenter 503 Service Unavailable error, the error can be caused by different factors:
- Some services have not loaded yet and are not running (one of the common issues is that the reverse Proxy service or the vSphere web client service is down).
- vCenter Server is on maintenance
- vCenter Server is overloaded
- Disk issues occurred on vCenter Server
- There are issues with a database used by vCenter
- Incorrect firewall settings (for vCenter installed on Windows) and network issues
You should find and fix the error on the vCenter server and not on the client side.
Services Have Not Started
If you have just started a vCenter instance, and all the needed services have not started yet, wait for a few minutes and try again.
- Try connecting to vCenter from another client.
If this doesn’t help, check whether all needed services have started.
- Open the Appliance Management Interface (for vCenter Server Appliance) in a web browser by entering the IP address or the FQDN (a Fully Qualified Domain Name) for vCenter and port 5480, for example:
https://192.168.101.103:5480/ui/services - Check the status of vCenter services in the Services section. For example, if the vSphere Web Client service is Started, and the vCenter Server service is Stopped, the VMware 503 Service Unavailable error can occur.
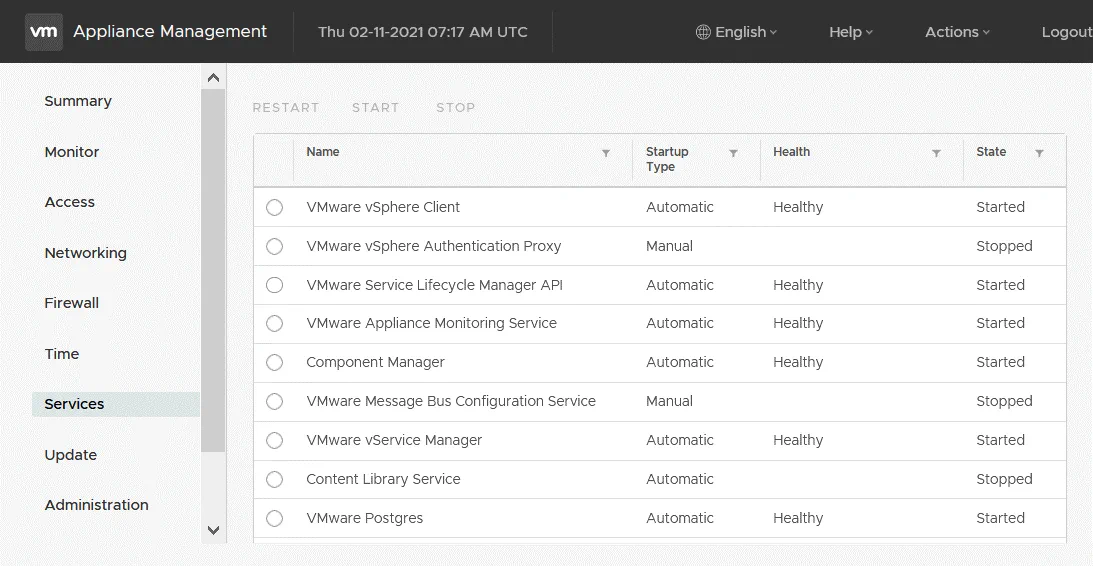
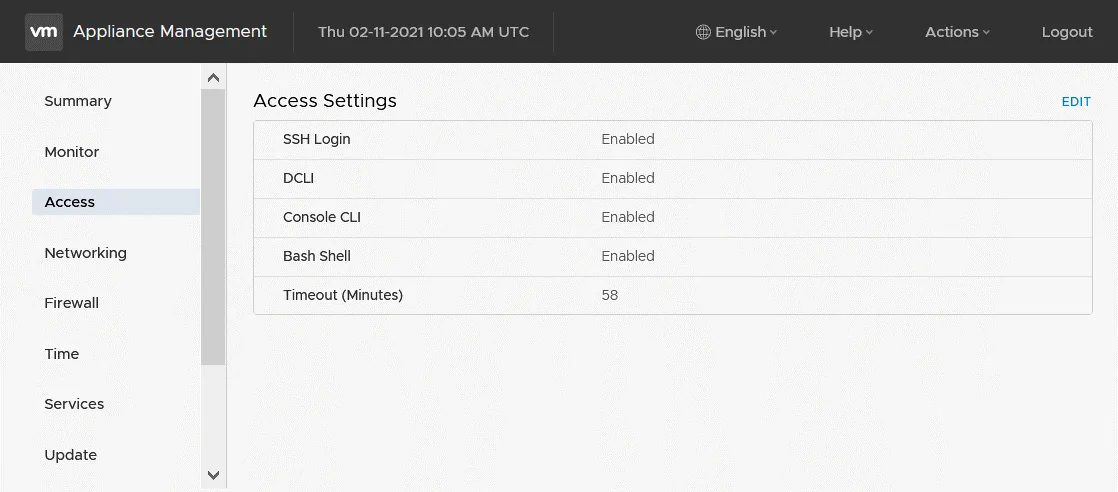
- You can check the status of vCenter services in the console and the command line interface (CLI). Enable SSH login, console CLI, and Bash Shell in the Access section of the vCenter Appliance Management Interface.
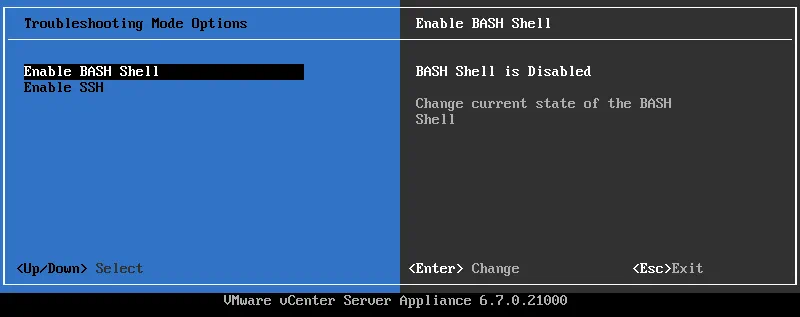
- As an alternative, you can enable Bash Shell and SSH access in the DCUI (Direct Console User Interface) of vCenter Server Appliance (VCSA) in the Troubleshooting Mode options.
-
Ensure that there is a connection between your computer and vCenter server by running the command from your computer (enter the host name or IP address of your vCenter):
telnet vcenter_fqdn 9443 - Connect to vCenter via SSH, or connect to the VCSA console (Press Alt+F1 in the DCUI of vCenter, log in, type shell, and press Enter).
-
Check the status of vCenter services by running the command on the machine running vCenter:
service-control --status --all
- If there is an external Platform Service Controller (PSC), check vCenter connection to the PSC. Check services on the PSC as well.
-
If some services have been terminated, run all services with the command:
service-control --start --all -
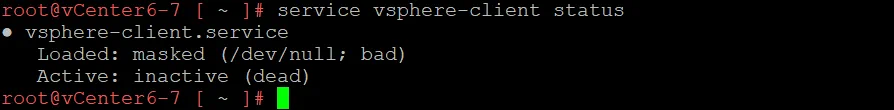
Try to stop and start the vSphere Client service:
service-control --stop vsphere-client
service-control --start vsphere-client - Wait about 10–15 minutes until the service starts, and then try to access vCenter in vSphere Client.
Check Log Files
Checking log files can help you find the cause of errors including the vCenter 503 Service Unavailable error.
First, investigate the vsphere_client_virgo.log file.
- For the Windows version of vCenter Server, logs are stored in:
C:\ProgamData\VMware\vCenterServer\logs\vsphere-client\logs\ - For vCenter Server Appliance, vCenter logs are stored in:
/var/log/vmware/vsphere-client/logs/
Also check the vpxd.log file.
- On vCenter running on Windows, vpxd.log is stored in:
C:\ProgramData\VMware\vCenterServer\logs\vmware-vpx\ - On vCenter Server Appliance, vpxd.log is stored in:
/var/log/vmware/vpxd/
Not Enough Free Hardware Resources
Insufficient disk space doesn’t cause the vCenter 503 Service Unavailable error itself. However, some services cannot start if there is no free disk space, and this may cause the 503 Service Unavailable error. High storage latency for vCenter may also be a reason of this error. Beginning from VCSA 6.5, the appliance is provided with 12 virtual disks (there were 2 virtual disks for VCSA before), and it’s possible that something may go wrong with one of the virtual disks. If vCenter Server is overloaded, the busy server cannot handle your request.
- Check free disk space, and run the command on the vCenter Server side. If you use vCenter Server Appliance, run this command:
df -h - The /storage/archive/ partition can be full in VCSA 6.7, and this is an expected (normal) situation based on VMware’s design of vCenter 6.7. Check free memory and processor resources:
top - Check the file system on the machine running vCenter. Use e2fsck to check the file system on VCSA, and run the command e2fsck -y filesystem, for example:
e2fsck -y /dev/sda1 - If errors are found and fixed, reboot the vCenter Server:
reboot
Issues with a vCenter Database
A database is an important component required for the proper operation of vCenter Server. If a database is not working, vCenter errors, including “vCenter 503 Service Unavailable”, may occur. Let’s explore possible database issues and methods of fixing them.
Sometimes the following errors are displayed in the vpxd log file:
An unrecoverable problem has occurred, stopping the VMware VirtualCenter service. Error: Error[VdbODBCError] (-1) “ODBC error: (23505) – ERROR: duplicate key value violates unique constraint “pk_vpx_vm_virtual_device”;
Error while executing the query” is returned when executing SQL statement “INSERT INTO VPX_VM_VIRTUAL_DEVICE
- If your vCenter is installed on Windows, check the Event viewer to see application event logs.
This is a bug due to duplicated entries in the embedded Postgres database that is used for the proper operation of vCenter.
- Open the command line interface of vCenter Server Appliance, and, for example, connect to the server via SSH.
- Go to the Postgres log directory:
cd /var/log/vmware/vpostgres - Check the log files. Log files are named in the postgresql-“dayofmonth”.log format. For example, the log file for the third day of the month is named “postgresql-03.log”. If today is the May 3, check the contents of the appropriate log file:
cat postgresql-03.log
2020-05-03 16:05:12.749 UTC 38a12db9.5481 1008636 VCDB vc ERROR: duplicate key value violates unique constraint “pk_vpx_vm_virtual_device”
2020-05-03 16:05:12.749 UTC 38a12db9.5481 1008636 VCDB vc DETAIL: Key (id, device_key)=(8101, 4002) already exists. - Remember the ID and DEVICE_KEY. In this example, these values are 8101 and 4002 respectively.
- Connect to the embedded Postgres database used by vCenter:
/opt/vmware/vpostgres/current/bin/psql -d VCDB -U postgres - Delete the duplicated entry:
DELETE FROM vc.vpx_vm_virtual_device where id=’8101′ and device_key=’4002′;“DELETE 1” in the output means that everything is OK.
- Exit the database CLI:
\q - Type reboot to reboot your vCenter Server. Wait until the vCenter Server and services have started, and try to open vSphere Client.
You may get the same error again after reboot. Check database logs again. If the duplicate entries were created again, delete them and reboot vCenter. You may need to repeat deleting duplicate entries and rebooting vCenter Server multiple times until the issue is resolved.
- Sometimes you may need to detect the affected VM, remove the affected VM from the inventory, then re-register (add) the VM to the inventory.
- If this method doesn’t help fix the issue permanently, try to upgrade your vCenter to vCenter 6.7 or newer.
- If you use the SQL database, check whether you have free disk space to store SQL database logs. If there is no free space on the SQL database logs filesystem, you may get the error.
Issues with Permissions
If your vCenter is installed on Windows Server, sometimes issues with account permissions may occur.
Check the “Log on as a batch job” policy in a group policy editor, and make sure that all needed accounts are present. Lack of permissions on Windows Server where vCenter is installed may cause the vSphere 503 Service Unavailable error.
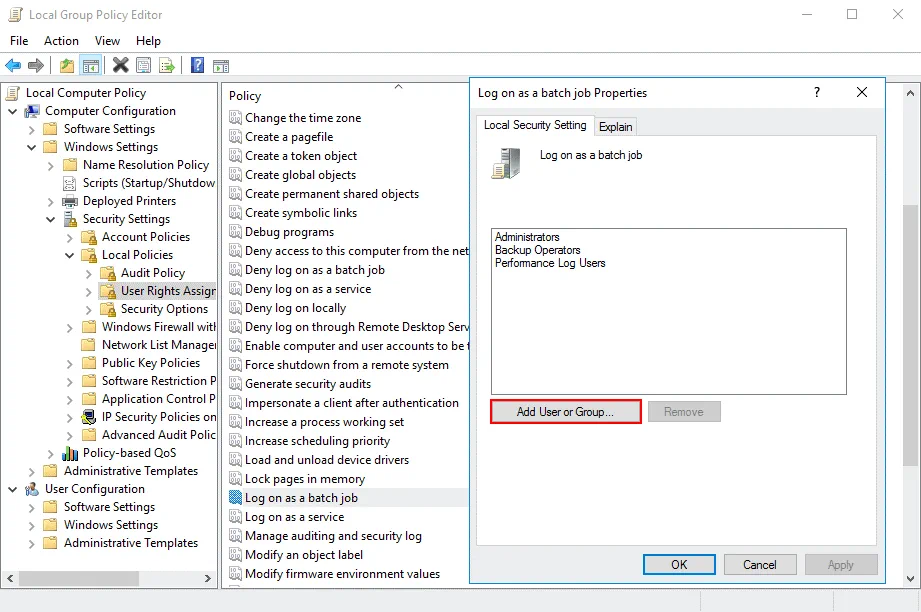
- Open the local group policy editor in Windows (Start > Run > gpedit.msc).
- In the group policy editor go to Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > User Rights Assignment > Log on as a batch job.
- Add these user accounts to this policy if they are missing:
cm
content-library
eam
imagebuilder
mbcs
netdumper
perfcharts
rbd
vapiEndpoint
vmware-vpostgres
vsan-health
vsm
vsphere-client
vsphere-ui - Click Add User or Group to add accounts.
- Stop and start the vSphere Client service by using these commands:
service-control –stop vsphere-client
service-control –start vsphere-client - Start the vSphere user interface service:
service-control –start vsphere-ui - Wait until the service is started.
- Reboot vCenter Server, and check whether vCenter is working correctly.
Usually the needed accounts should be added by the installer of vCenter automatically until this policy is set manually in a group policy editor.
Network and DNS Issues
Make sure that a DNS name of vCenter is set correctly and the IP address of vCenter Server is resolved. If DNS has a wrong entry, you may get the 503 Service Unavailable error. When you install vCenter, set the DNS name in the configuration at step 7 (Configure network settings) of stage 1.
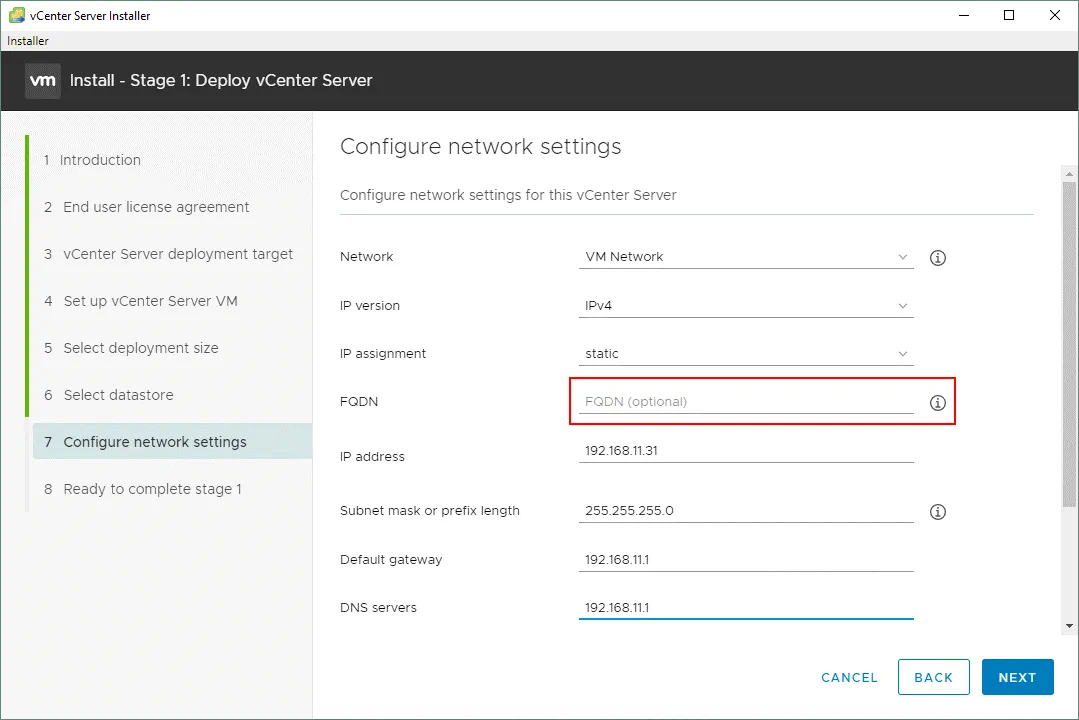
If you are using an external PSC, the PSC IP address must be resolved in both directions – forward lookup and reverse lookup.
- Check the hostname in /etc/hosts on the vCenter Server Appliance. Make sure that a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) and a short name are present in this file in the following format:
vCenter_IP vCenter Server Appliance FQDN vcenter short name
For example:
192.168.101.103 vCenter6-7.vsphere.local vCenter6-7 - After changing the DNS configuration, restart the vpxd service:
service vmware-vpxd restart - You can check the status of the vpxd service with the command:
vpxd status service vmware-vpxd status - On the PSC run these commands to restart related services:
/etc/init.d/vmware-stsd restart
/etc/init.d/vmware-sts-idmd restart
service vmware-cm restart - Restart the vpxd service on the machine where vCenter is installed:
service vmware-vpxd restart - Wait until all needed services have started, and try to open VMware vSphere Client.
It is recommended that you use a vCenter deployment model with an embedded PSC to have less network issues. The latest versions of vCenter, like vCenter 7.0, only support installation with an embedded PSC.
If you still get the vCenter 503 Service Unavailable error, try the next method.
- Try to enable or disable IPv6. Open /etc/sysctl.conf and change the net.ipv6.conf.eth0.disable_ipv6 from 1 to 0 to enable IPv6:
#Disabling SLAAC/Link Local addresses
net.ipv6.conf.eth0.disable_ipv6=0 - Similarly, set 1 to disable IPv6.
- Once you save settings, run the commands:
sysctl -a
sysctl -p - Open VMware vSphere Client now. Check whether everything is working properly after reboot.
- Try to disable SMBv1 and enable SMBv2 instead. Then restart vCenter Server and check whether this method has helped.
Password Issues
Check whether your root password for vCenter Server Appliance has expired. If it’s expired, you won’t be able to log in to vCenter to edit configuration and fix errors including the vCenter appliance 503 Service Unavailable error without a workaround. You can set the root password expiration period to 0 if you want a password to never expire.
- You can edit the root password expiration settings in the GUI of vCenter Server Appliance Management:
https://your_vCenter_IP:5480/ui/administration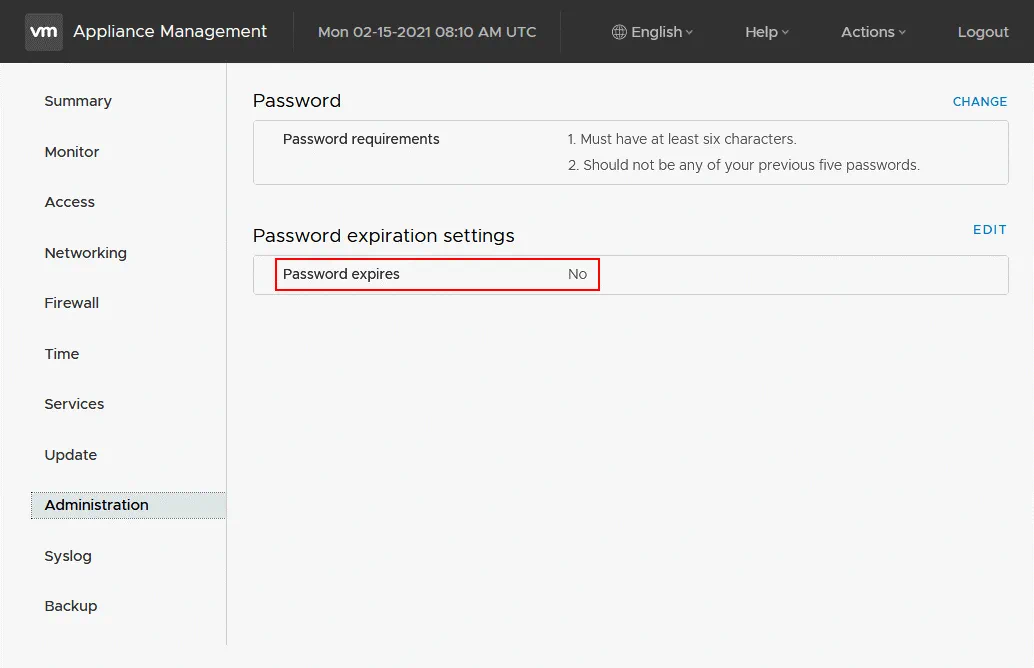
- If there is password mismatch in vmdird for the account specified in vmdird-syslog.log, this factor may be a reason of getting the following error:
503 Service Unavailable (Failed to connect to endpoint: [N7Vmacore4Http20NamedPipeServiceSpecE:0x7f3d084a60c0] _serverNamespace = / _isRedirect = false _pipeName =/var/run/vmware/vpxd-webserver-pipe)”
- Check the /var/log/vmware/vmdird/vmdird-syslog.log file to identify which account password is invalid and must be reset.
Note: Back up your vCenter before editing configuration or at least take a snapshot if your vCenter Server is running on a virtual machine. Do the same for the external Platform Service Controller if you are using one. - Log into vCenter Server Appliance as root via SSH. Type shell.set –enabled true and type Shell to access the Bash console.
- Open the vdcadmintool tool by running the command:
/usr/lib/vmware-vmdir/bin/vdcadmintool - Select the third option:
Reset account password - Enter the name of the account, the password of which you want to reset, according to the information in the vmdird-syslog.log file.
- A new password is generated automatically. Copy and note this password.
Note: If you see a blank character in the password, generate a new password by going back to the previous step. This issue occurs if a password contains special characters, and they are displayed as missing (blank) characters. - Connect to vCenter Server via SSH as explained above (if you are using an external PSC). If you are using the embedded PSC, go to the next step.
- Run the command to update the new password:
/opt/likewise/bin/lwregshell
cd HKEY_THIS_MACHINE\services\vmdir\
set_value dcAccountPassword “new password”
quit - Restart the vCenter Server Appliance services by using the commands:
service-control –stop –all
service-control –start –all
Perform vCenter Backup
It is generally recommended that you back up vCenter after finishing configuration. You should do that after ensuring that vCenter is working correctly and before editing configuration to make it possible to restore vCenter if something goes wrong. The best approach is creating regular vCenter backups because vCenter configuration may change during operation and some items may be added to the vCenter inventory. You cannot predict when a failure will happen.
NAKIVO Backup & Replication is a universal data protection solution that can back up VMware vSphere VMs and physical machines running Windows and Linux, including SQL databases. Protect your vCenter Server machines with NAKIVO Backup & Replication, and, if something goes wrong with your vCenter, you can restore the working configuration in a short time. Support of incremental backup and the GFS retention policy helps perform VMware vCenter backup more rationally. The product supports SQL log truncation to save storage space and reduce the probability of errors caused by insufficient disk space with large database logs.




