How to Take Snapshot of EC2 Instance for AWS EC2 Data Protection
If you’re using Amazon Web Services (AWS) to run EC2 instances (VMs) in Elastic Compute Cloud, you have several ways to protect your workloads against data loss caused by software failure, malware infection, accidental deletions, among other things. One option available to you is the AWS built-in backup feature for EC2 instances called EBS snapshots. This blog post explains how to create a snapshot of an EC2 instance by using EBS volume snapshots with detailed examples of the configuration process.
What Are EBS Snapshots?
EBS snapshots are incremental copies of an Elastic Block Store (EBS) volume that are stored in Amazon S3. This means that when you create an EBS snapshot for the first time, a full backup is created, and only changed data is copied for the subsequent EBS snapshots. EBS volumes are virtual disks attached to EC2 instances.
Even though EBS snapshots are stored in Amazon S3, you cannot access the snapshots in S3 storage manually. You can manage these snapshots in the EC2 Management Console.
Note: The terms AWS EC2 snapshot and Amazon snapshot are sometimes also used to refer to EBS snapshots.
How EBS snapshots work
EBS snapshots are block-level backups of EC2 instance data that represent the EBS volume at the specific point in time when the snapshot command was issued. This means that if the instance is running, the data blocks written to EBS volumes after the initiation of the snapshot-taking are not saved to the snapshot. As a result, EBS snapshots are crash-consistent and not application-consistent backups.
Note that EBS snapshots are not the same as snapshots in the context of VMware vSphere and Microsoft Hyper-V. Hyper-V and VMware snapshots are not backups and cannot replace proper backups.
However, there are limitations to EBS snapshots, which include lack of scheduling and retention options, no possibility to create on-premises copies, as well as the complexity of creating an application-consistent EC2 snapshot to simplify recovery.
How to Create Snapshot in AWS Console for EC2 Instances
AWS Management Console is the GUI web interface used to manage all AWS computing, storage, and other resources, including creating EBS snapshots.
To access the EC2 instance for which you want to create a snapshot:
- Sign in to AWS Management Console by using an account that has the required permissions for creating EC2 instances, EBS volumes, and EBS snapshots.
- Click Services and in the Compute section, click EC2 to open the management console for EC2 instances, EBS volumes, and other EC2 features.
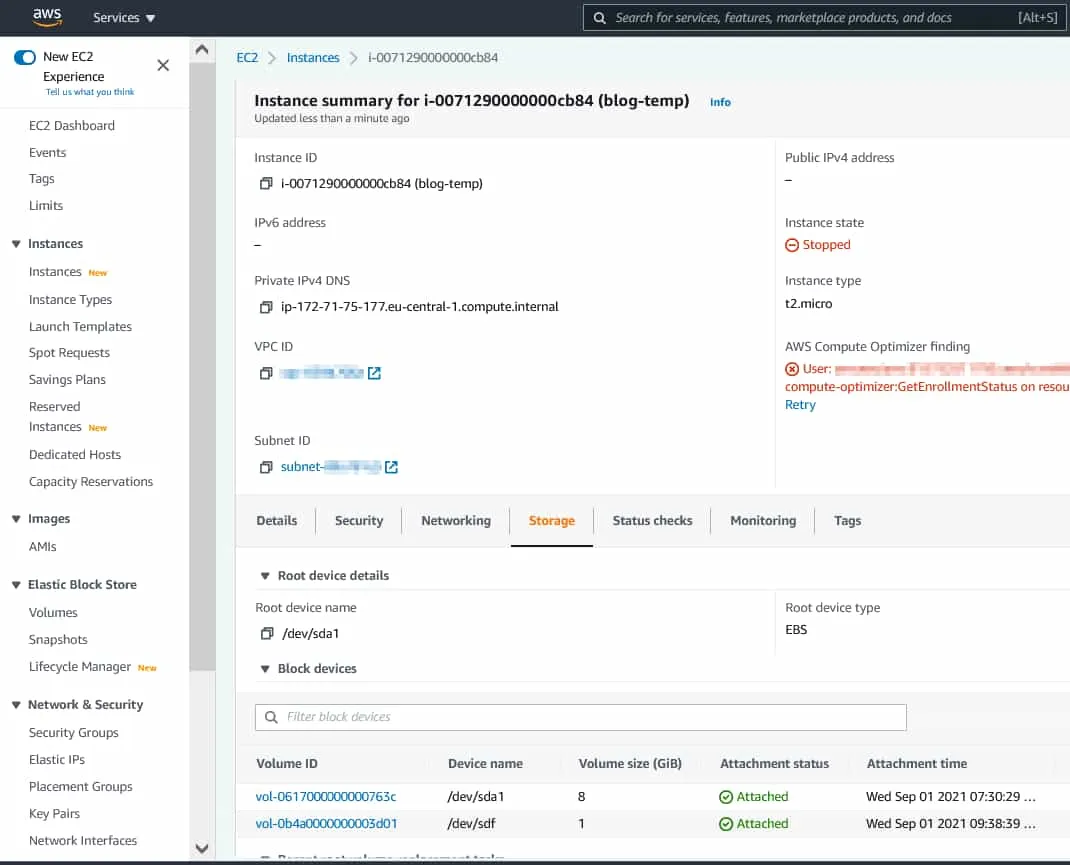
We have prepared an EC2 instance to demonstrate the steps to create EBS snapshots. The parameters of our EC2 instance, which we are going to back up and recover using EBS snapshots, are the following:
Name: blog-temp
EC2 instance ID: i-0071290000000cb84
Instance type: t2.micro
Availability zone: eu-central-1c
EBS Volume 1: vol-0617000000000763c
Volume type: gp2
Volume size: 8 GB
The guest operating system (OS) running on the EC2 instance is Ubuntu Server (Linux).
Writing files to the EBS volume
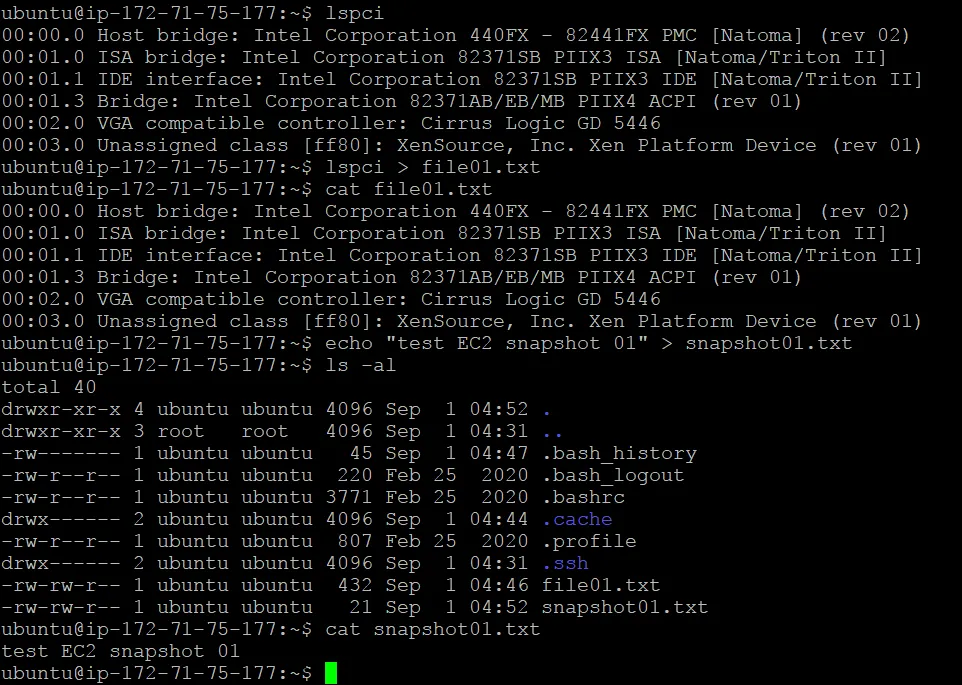
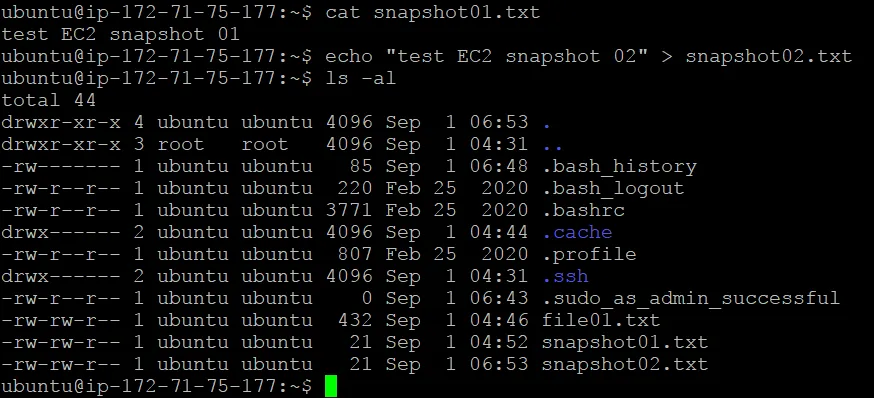
Let’s create two files on the virtual disk attached to the EC2 instance before creating a snapshot. This way, we can check whether these files are recovered after restoring the instance from the EBS snapshot. We create two files in the user home directory:
lspci > file01.txt
echo "test EC2 snapshot 01" > snapshot01.txt
Preparing the instance
Stop the EC2 instance to make sure that the snapshot contains consistent data. The reason for this is that EBS volumes work at the block level. When an EBS snapshot is taken, the EBS volume state for that moment in time is saved. Storage blocks are saved as is. The system is not aware of operations made with files at the file system level at that time. If files are being written on an EBS volume when a snapshot is taken, the snapshot will contain inconsistent data. The effect is similar to unplugging a power cable from a physical computer while files are being written.
If you want to take a snapshot of a non-system EBS volume, you can unmount the file system from the operating system to ensure that there are no file-writing operations on the volume. Hibernation must be disabled for the EC2 instance to take a snapshot.
To prepare your EC2 instance for taking a snapshot:
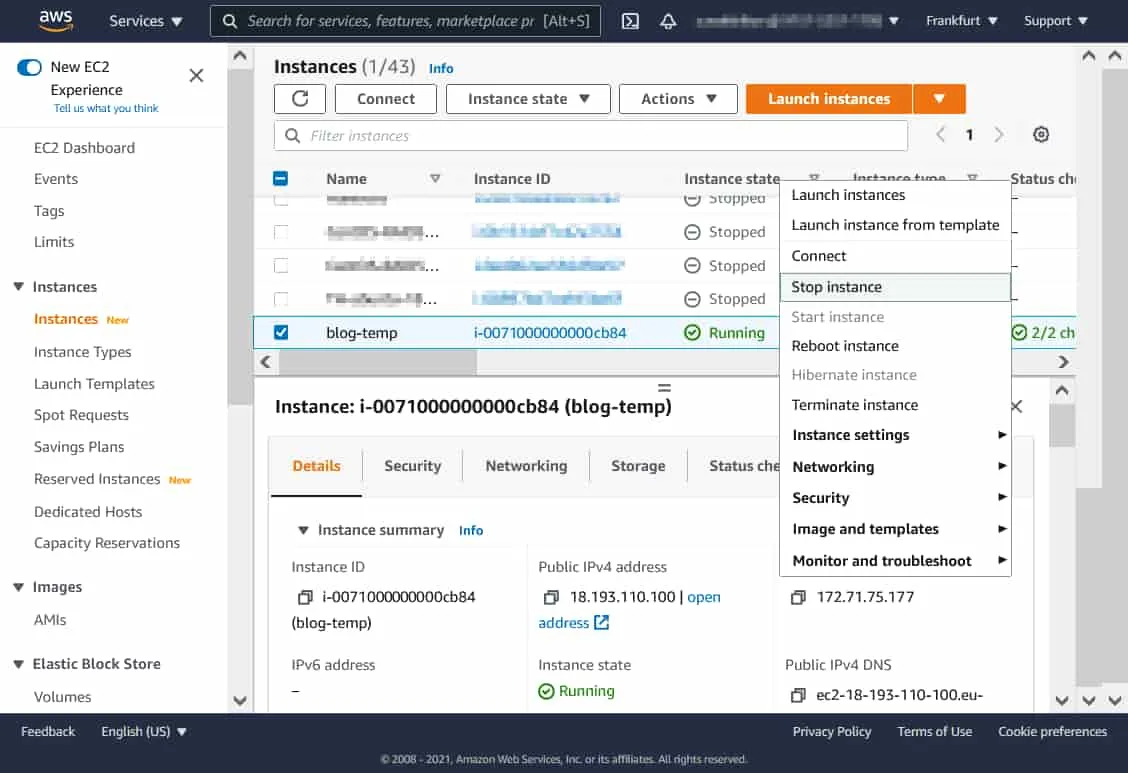
- Open the page with the list of EC2 instances in the EC2 management console. Right-click the instance name and, in the context menu, click Stop instance.
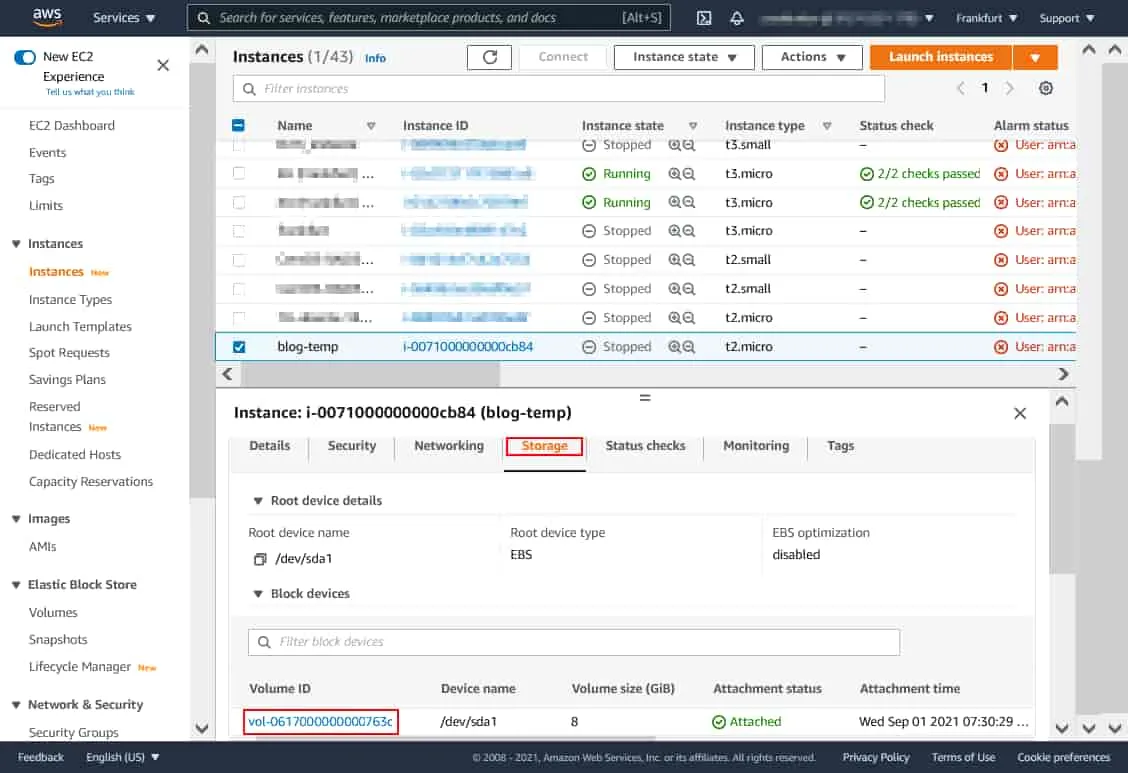
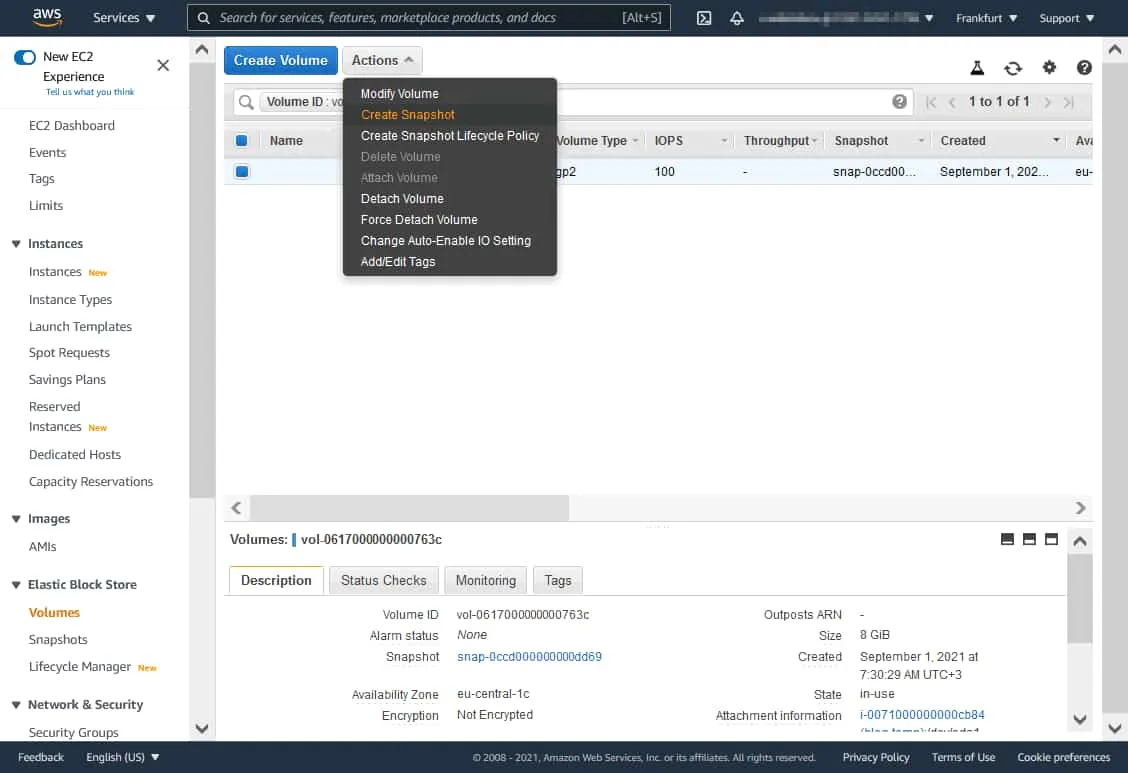
- Locate the volume used by the EC2 instance. Click the Storage tab and click the volume ID of the appropriate EBS volume (vol-0617000000000763c in our case).
Taking a snapshot
We are ready to create snapshot of EC2 instance:
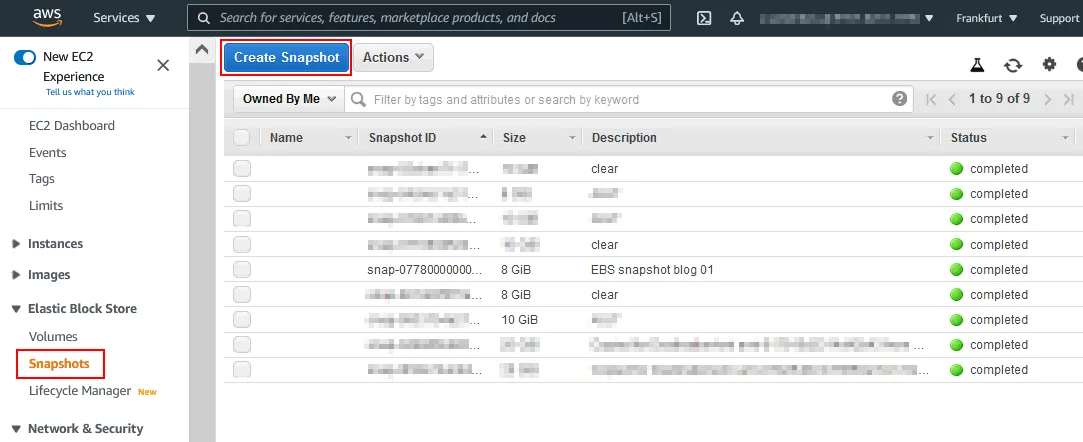
- Select the EBS volume (click the checkbox on the left side of the line) and click Actions > Create Snapshot.
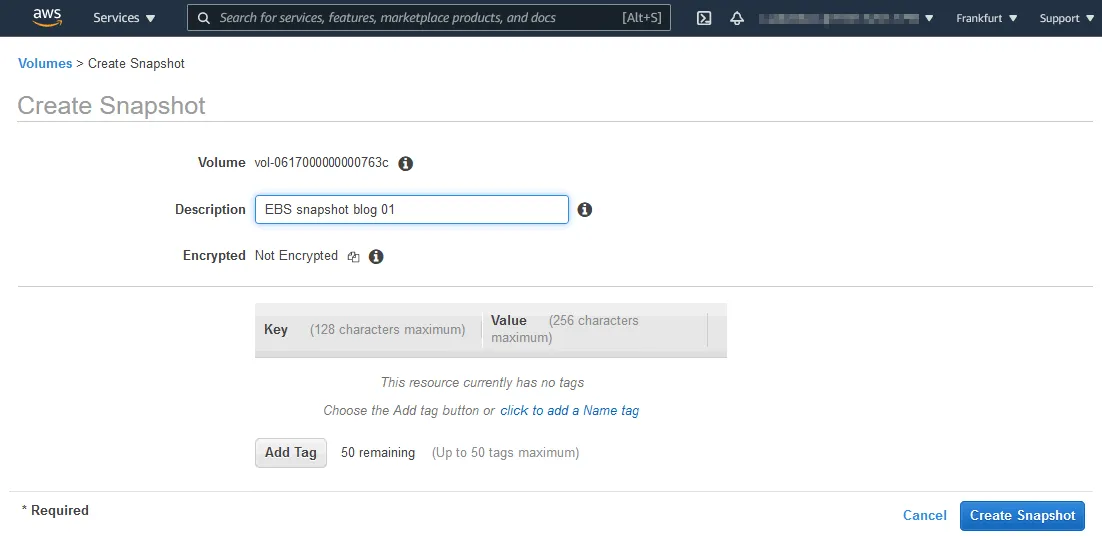
- Enter a description, set the encryption settings, and add a tag. I use the following parameters:
- Description: EBS snapshot blog 01
- Encryption: Not encrypted
Click Create Snapshot.
Note: We use the unencrypted volume and create an unencrypted snapshot. In this case, encryption settings for the snapshot can be set manually. When you take a snapshot of an encrypted volume, the snapshot is encrypted automatically.
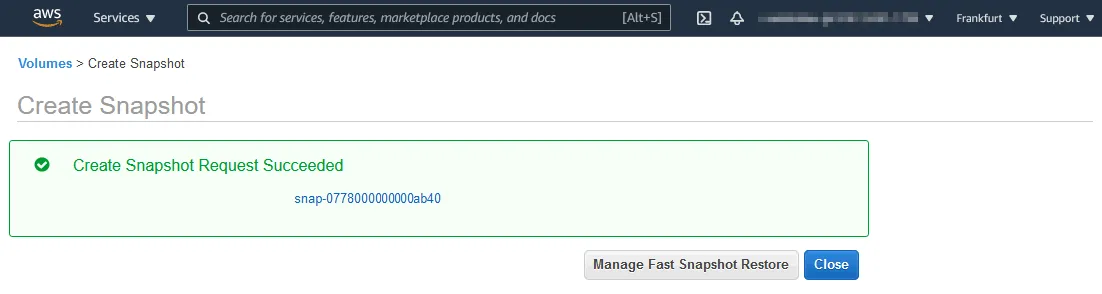
- You should see the following message and the snapshot ID:
Create Snapshot Request Succeeded
snap-0778000000000ab40
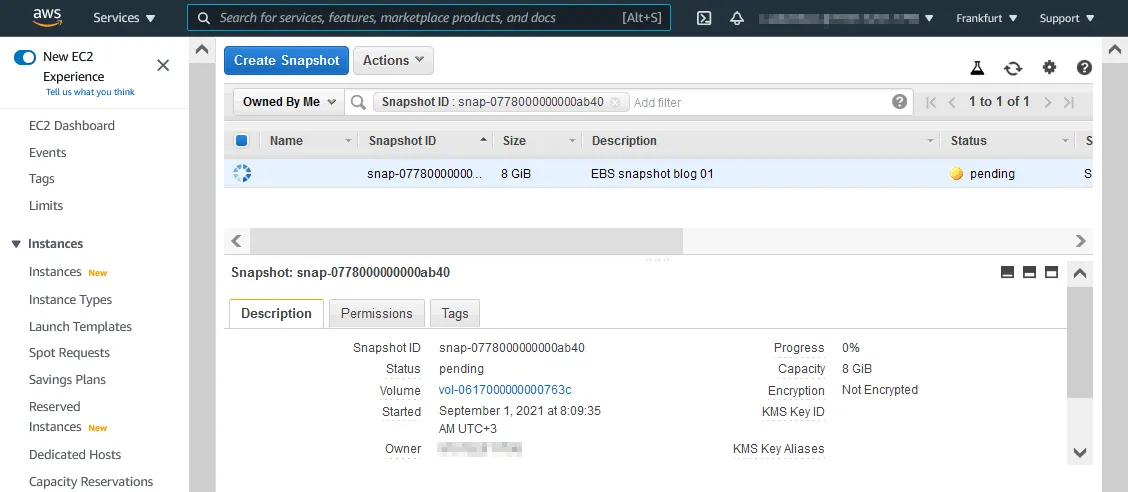
Click the snapshot ID to open a page with the snapshot options and status.
- The pending snapshot status means that data from the EBS volume is being transferred now to Amazon S3. Wait for snapshot creation to be completed (the status is changed to completed). The time depends on the size of data saved to the snapshot.
How to Take Multi-Volume Snapshots
It is common to find an EC2 instance using multiple EBS volumes. In this case, you can create a multi-volume snapshot for all EBS volumes attached to that EC2 instance for an Amazon EC2 backup.
In this section, we’ll cover:
Creating a second EBS volume for the EC2 instance
Let’s first add a second EBS volume to our EC2 instance, which we are using for demonstration purposes:
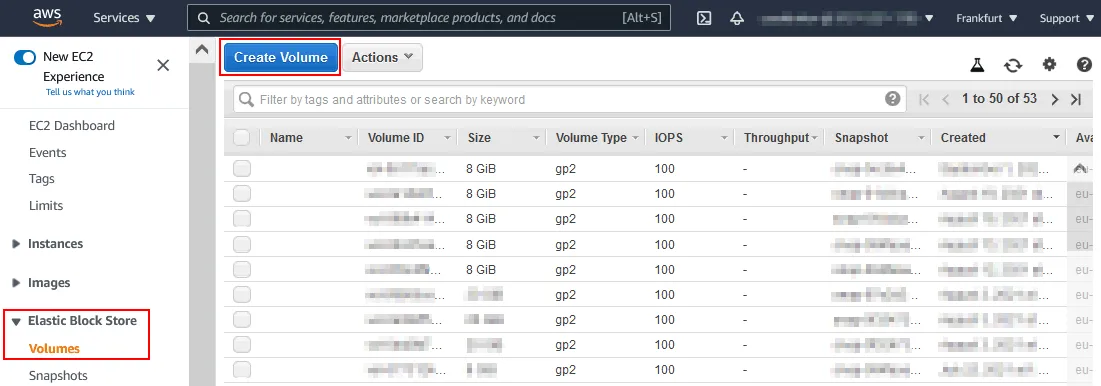
- In the navigation pane of the EC2 management console, go to Elastic Block Store > Volumes. Click Create Volume.
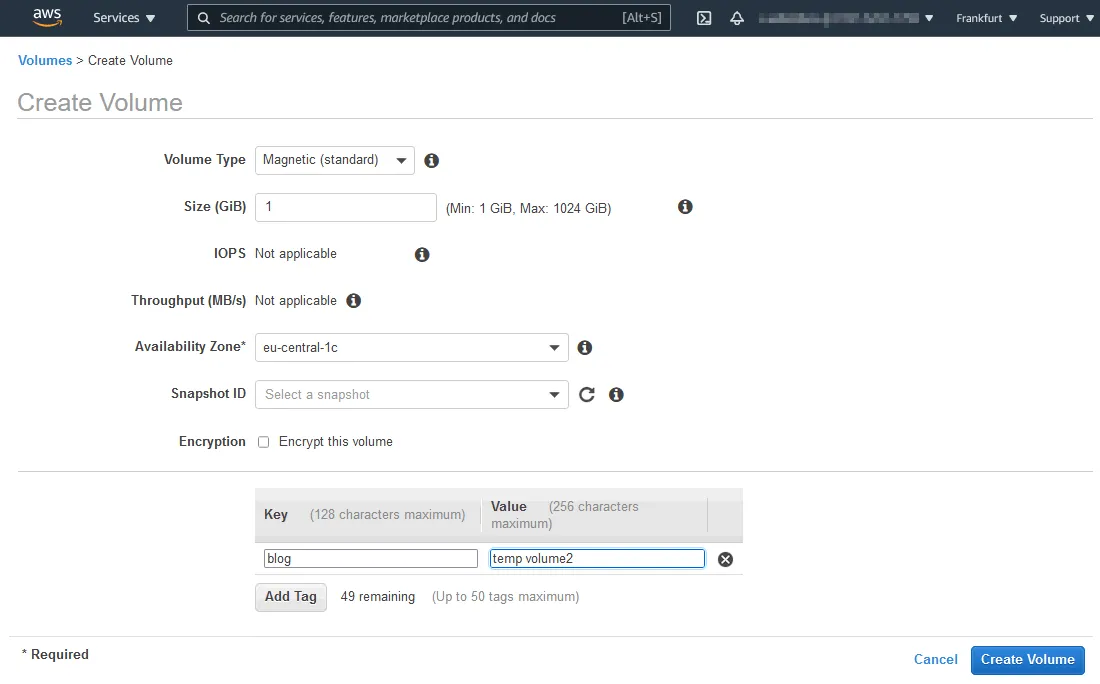
- For Availability Zone, the region must be the same as the region of the instance (eu-central-1c in our case).
Enter the volume type/size, set the encryption options, and enter tags. Tags help find the volume in the list of volumes. We set the volume size at 1 GiB, and use the following tags:
-
Key: blog
-
Value: temp volume 2
Click Create Volume.
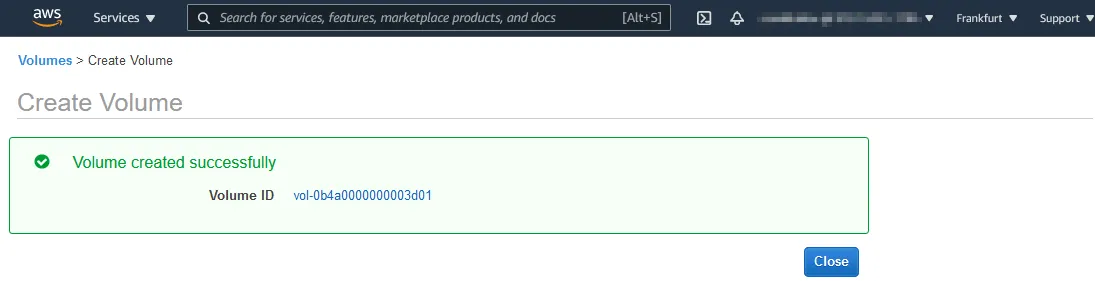
- Remember (or write down) the id of the volume (vol-0b4a0000000003d01 in our case). Click the volume ID to open the volume properties.
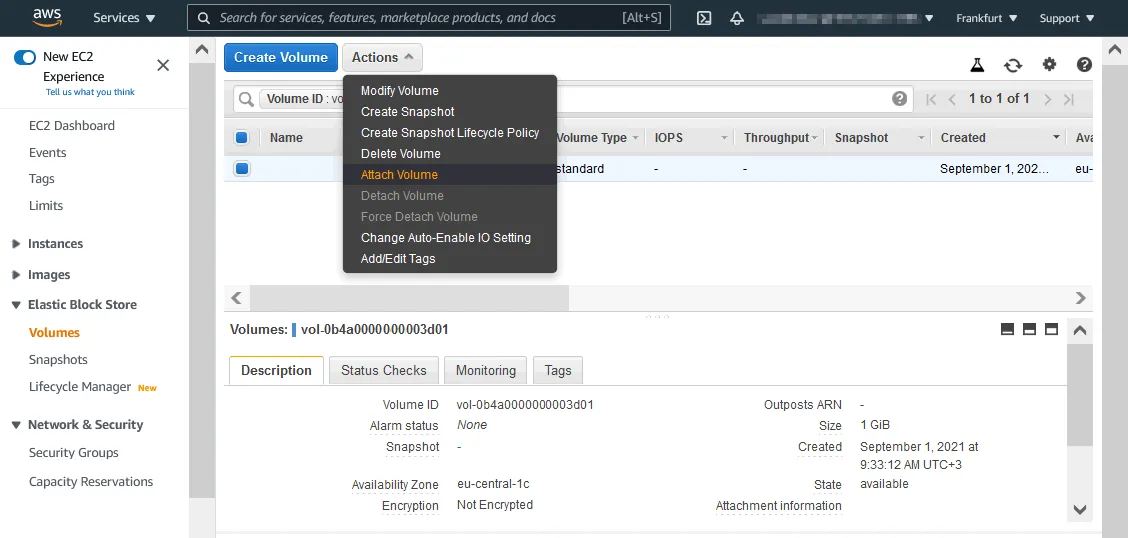
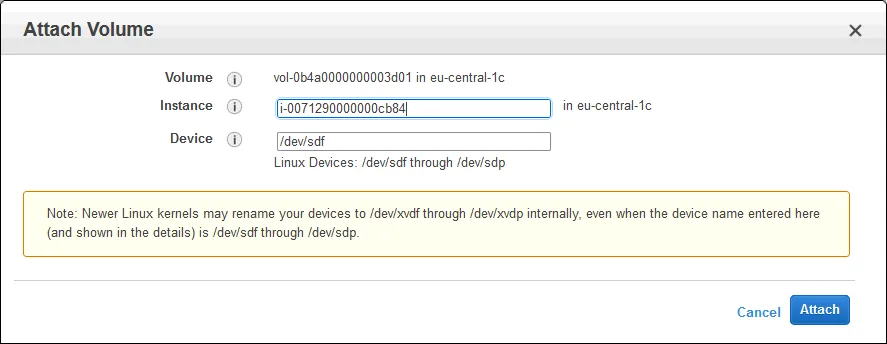
- Attach the volume to the EC2 instance. Right-click the volume or click Actions and, in the menu that opens, click Attach Volume.
- Select the instance to which you need to attach the EBS volume. You must select the EC2 instance ID. In our case, the instance ID is i-0071290000000cb84.
You can select the device in the guest operating system used to access the attached volume. In our case /dev/sdf is used.
Click Attach to attach the new volume to the EC2 instance.
Note: Useful information about renaming disk devices is displayed in the note. In our case /dev/sdf is renamed to /def/xvdf in the guest OS.
Two volumes are now attached to our EC2 instance (blog-temp):
vol-0617000000000763c
vol-0b4a0000000003d01
Writing data on the second EBS volume
Next, we will create a file on the second EBS volume. This file will be used to check whether all the data is recovered after restoring the volume from the EBS snapshot. For this reason, we will create a partition, create a file system, and mount the file system to the guest Linux OS running on the EC2 instance.
Even though we are focused on operations with EBS snapshots rather than operations in the guest Linux OS running on the EC2 instance, we list the commands used to better understand operations with volumes.
Managing storage
- Use lsblk to display details about block devices in Linux.
- Use df -h to check storage space on mounted disks.
- Use mount to check mounted disks.
Creating and mounting a partition
Creating and formatting a partition on the second EBS volume in parted:
sudo parted -l
parted /dev/xvdf
(parted) mklabel msdos
(parted) print
(parted) mkpart primary ext4 1MB 955MB
(parted) print
(parted) quit
Creating a file system on the prepared partition:
mkfs.ext4 /dev/xvdf1
Creating the directory to use as the mount point:
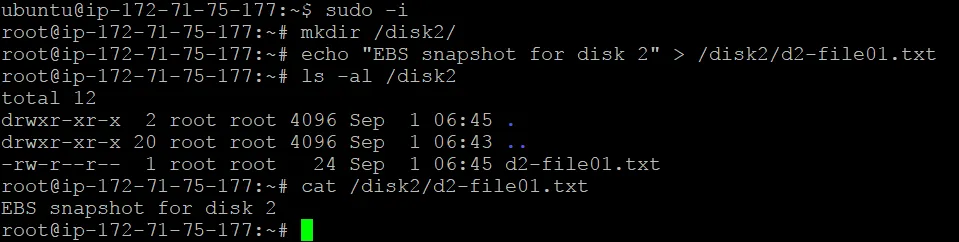
mkdir disk2
Mounting the partition with the file system to the created directory:
mount /dev/xvdf1 /disk2/
Going to the directory of the mounted partition:
cd /disk2
Writing changes to the 2 EBS volumes
- Create the file on the partition located on the second EBS volume attached to the EC2 instance running Linux:
echo “EBS snapshot for disk 2” > /disk2/d2-file01.txt
- Make changes on the first disk to create a new EBS snapshot of the first volume used by the EC2 instance. Both volumes should contain changes from the state when the previous snapshot was taken.
We create the snapshot02.txt file on the first volume to more conveniently detect changes saved to the new snapshot of the first volume.
Once the two EBS volumes with new data are attached to the EC2 instance, we can create multi-volume snapshots.
Creating the multi-volume snapshot
- Go to Elastic Block Store > Snapshots in the navigation pane of the EC2 instances management page. Click Create Snapshot.
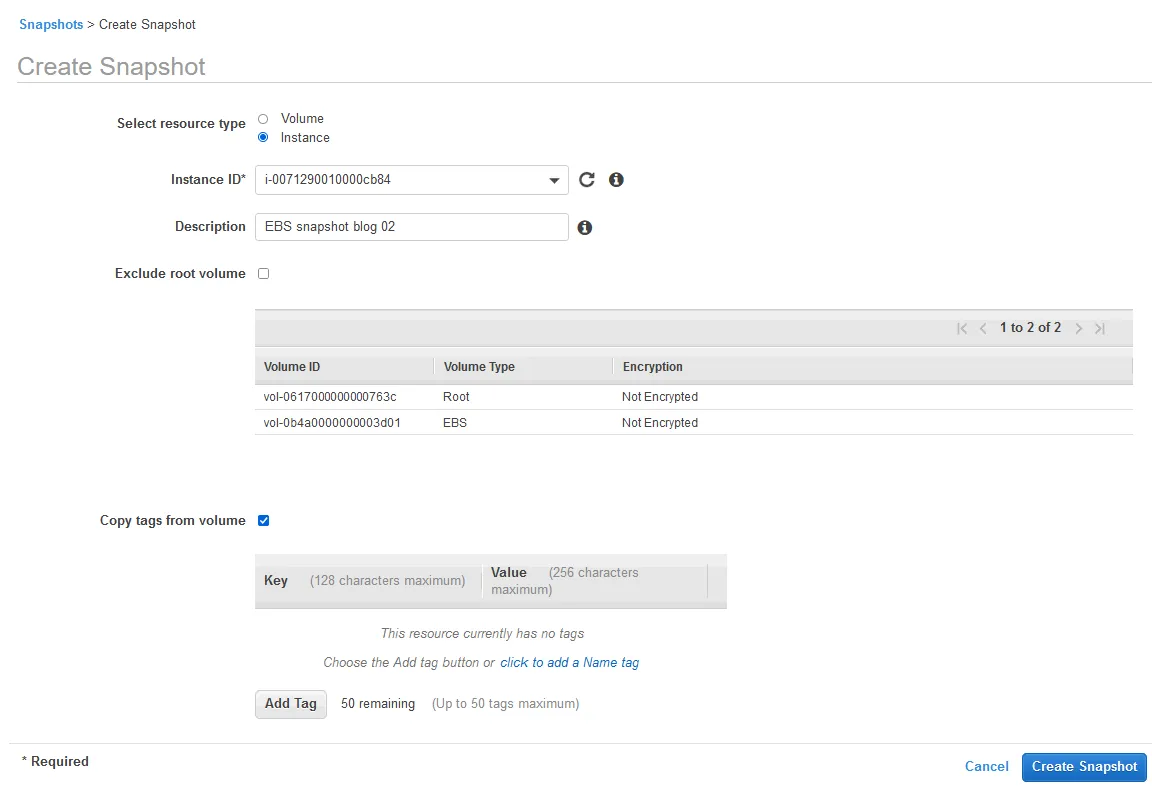
- Select resource type: Instance.
- Enter the instance ID of the needed EC2 instance whose volumes you want to back up by using EBS snapshots.
All volumes attached to the selected instance are selected automatically.
- Enter a description to help you find the EBS snapshot in AWS when needed. In our example, the description is EBS snapshot blog 02.
- Select the Copy tags from volume checkbox if you want to use the tags assigned to EBS volumes.
- Once hit Create Snapshot, snapshots for all selected volumes are created.
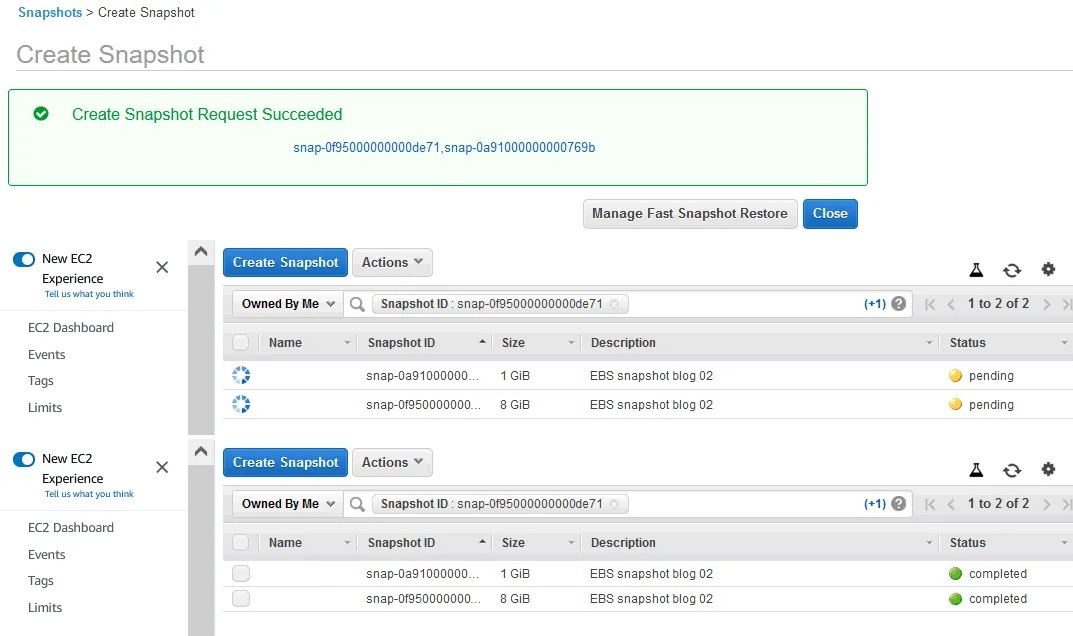
If the process is successful, you’ll see the following message:
Create Snapshot Request Succeeded
Two Amazon snapshot identifiers are displayed: snap-0f95000000000de71 and snap–0a91000000000769b in our case.
You can save these ID values and click one of them to check the snapshot creation status. Right after initiating the snapshot creation, the operation status is pending and changes to completed once the process is over.
A new snapshot for each volume has been created.
Using AWS CLI to Create Snapshots
You can use AWS CLI as an alternative to AWS Management Console if you prefer the command-line interface or you need to automate snapshot creation.
The command to create an EBS snapshot in AWS CLI is:
aws ec2 create-snapshot --volume-id vol-0b4a51e1cea333d01 --description "This is a test snapshot for the blog"
The output should look like this:
{
"Description": "This is a test snapshot for the blog",
"Tags": [],
"Encrypted": false,
"VolumeId": "vol-0b4a51e1cea333d01",
"State": "pending",
"VolumeSize": 8,
"StartTime": "2021-08-28T21:06:01.000Z",
"Progress":