How to Recover Deleted OneDrive Files: 7 Methods
Organizations using Microsoft OneDrive as cloud storage can face different data loss challenges, including accidental deletion of OneDrive items. Other reasons for OneDrive data loss can be malware or intentional unauthorized actions of a malicious actor. Can deleted OneDrive files be recovered? The answer is yes, you can recover deleted files in OneDrive under certain circumstances.
In this blog post, we explain how to recover deleted files from OneDrive. Native Microsoft 365 features provide different methods for data recovery. However, you should consider implementing a third-party data protection solution to enhance the resilience and recoverability of your OneDrive and other Microsoft 365 data.
Understanding File Deletion in OneDrive
When you accidentally or intentionally delete an item from OneDrive storage, that item does not get completely wiped out. First, the item you delete is moved to the OneDrive Recycle Bin. In that recycle bin, items remain available for 30 days after initial deletion. Also, depending on the settings, the deleted OneDrive items can be sent to the local recycle bin on your device.
7 Methods to Recover Deleted Files in OneDrive
There are several methods to recover OneDrive deleted files, including working with the recycle bin (both primary and secondary levels), local storage, and versioning. Below, we cover different methods for recovering OneDrive deleted files using native tools.
However, when you consider organizing data protection and recovery for your Microsoft 365 environment, keep in mind their shared responsibility model and don’t limit your recovery capabilities with exclusively native features. Microsoft recommends implementing a third-party backup solution for better reliability, so below you can also find the method involving a third-party solution to recover deleted files from OneDrive.
Method 1: Use the Search feature to find your files
First, you can check if the required items have been actually deleted. Use the OneDrive search to simplify the process:
- Log in to your OneDrive account.
- Enter the missing item’s name into the search bar, then hit Enter. Wait for the results to be displayed.
- If your item shows up, continue using it as planned. If the system can’t find the required item, proceed with the methods below to recover your deleted files in OneDrive.
Method 2: Recover permanently deleted files from your device
After you delete items from OneDrive, check your Recycle Bin (Windows) or Trash (Mac). The deleted files can be there.
Note the following:
- When you delete OneDrive online-only items, they don’t appear in your device’s Recycle Bin or Trash folder.
- The message [Folder name] was removed from your OneDrive means that a shared folder was deleted. Restoring a folder that another OneDrive user shared with you is not possible after deletion. If you have shared a folder with other OneDrive users and they delete items from there, the items go to your OneDrive Recycle Bin.
To restore items from the Windows Recycle bin, you need to:
- Open the Recycle Bin.
- Choose the required items (folders or files).
- Right-click those items.
- In the context menu, hit Restore.
For Mac, the procedure is as follows:
- Open the Trash.
- Choose the items to recover.
- Right-click those items.
- In the context menu, hit Put back.
After that, files or folders from your Recycle Bin or Trash get restored to the original location.
Method 3: Use OneDrive Recycle Bin to recover items
The first method to recover items is to use OneDrive Recycle Bin. If you can’t locate the required OneDrive items in the Windows Recycle Bin (either because you haven’t set such deletion options or the items just aren’t there), you can try to recover them from the online version of OneDrive.
- Enter your credentials to Microsoft 365, then choose OneDrive from the list.
- In the navigation page on the left, find and hit Recycle bin.
- Choose the items to recover (click the circle to the left of each item), right-click the items to open the context menu, and then hit Restore.

Method 4: Recover files from the Second-stage Recycle Bin
If you cannot find the deleted files in the Recycle Bin, check the second-stage recycle bin. Deleted items are moved from the Recycle Bin to the second-stage recycle bin 30 days after deletion.
In order to open the Second-stage recycle bin, open the Recycle Bin in the OneDrive web interface, scroll down the page, and click the Second-stage recycle bin link at the bottom of the page.
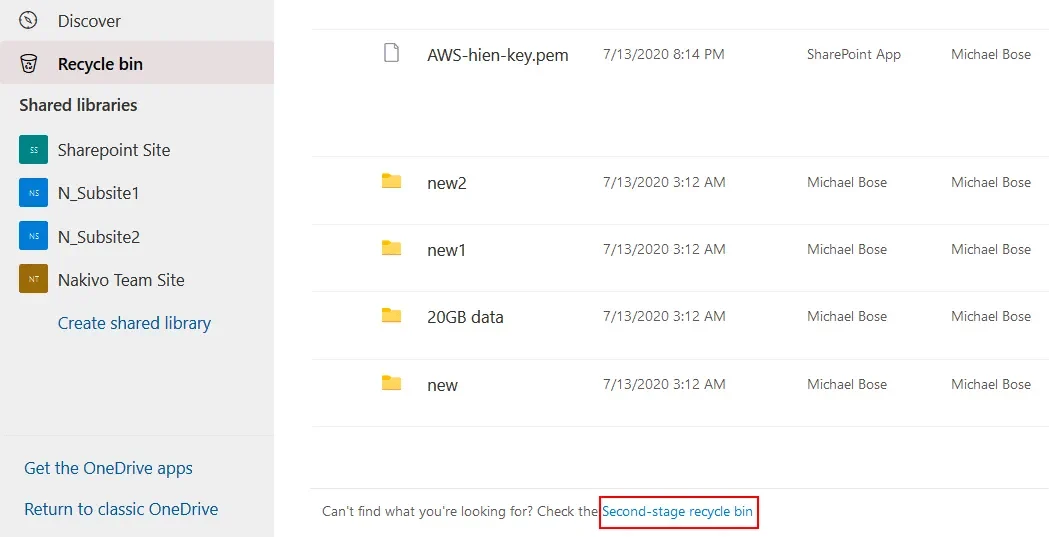
Once the second-stage recycle bin opens, look for the items that you want to recover, select them, right-click the items, and, in the context menu, hit Restore. Another option is to hit the Restore button in the top panel of the page.
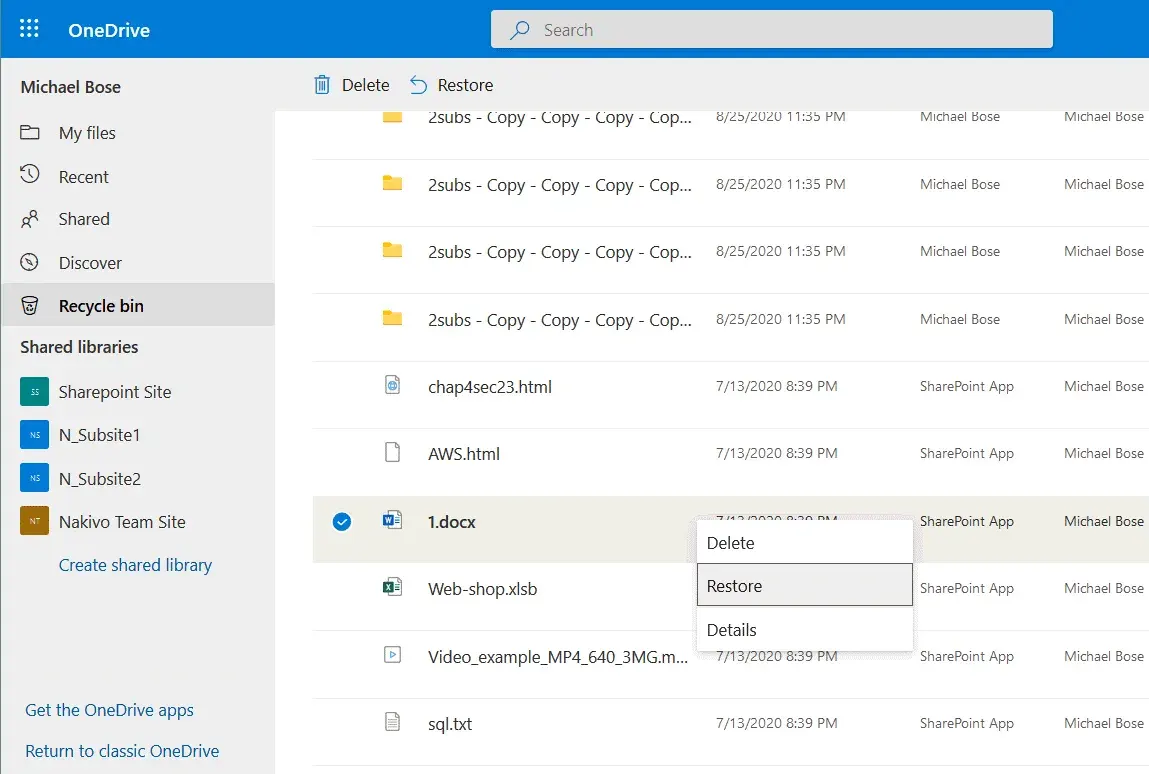
With this native functionality, you can also restore custom versions of files stored on OneDrive.
Method 5: Recover OneDrive files from a local backup
OneDrive can create a folder on your device’s storage disk to keep items there. This way, the files you upload to OneDrive can get to the cloud storage and to a local directory as a backup folder.
In case the items you need are not in cloud storage, check whether they are in that local directory. To do so, follow the steps below:
- On the System Tray, right-click the Microsoft OneDrive icon.
- Go to Settings > Account > Choose folders.
- Locate the OneDrive folder.
- Paste the location path into the File Explorer’s search bar.
- Browse for the required files there.
Method 6: Restore the OneDrive point-in-time state
You can restore items to their point-in-time state, which enables also recovering deleted files from OneDrive.
- Sign in to your OneDrive account.
- Find Settings > Options. For corporate or educational accounts, the path is Settings > Restore your OneDrive.
- Choose Restore your OneDrive > Verify your identity.
- Choose the required date, then hit Restore.
OneDrive then restores the state of your cloud storage to the specified date, including the deleted files. This feature enables you to undo changes in OneDrive applied within the last 30 days.
Method 7: Using a Third-Party Recovery Solution
Native Microsoft tools have limited recovery capabilities which can work for an individual but not an organization. Specialized third-party solutions to back up and recover OneDrive deleted files have extended feature sets that add data reliability and simplify management.
Modern data protection solutions enable you to schedule and automate OneDrive backup workflows across your organization’s environment. Then, you can send the backup data from OneDrive to multiple onsite and offsite storage locations for improved availability. Such solutions also provide security features to protect backups from malware and unauthorized access. Lastly, you can use flexible recovery options to recover deleted files in OneDrive to their original location or send them to another destination within minutes.
Preventing OneDrive Data Loss: 7 Best Practices
To prevent losing OneDrive data or mitigate the consequences of such losses using both native tools and third-party solutions, consider the following recommendations.
Identify the data to protect
Microsoft 365 offers a set of features to monitor activities, users, and cloud storage space. This allows you to find out the amount of data that you should protect. This information helps you understand the required capacity of your backup storage.
NOTE: The overall price of a backup storage and the workflows to restore OneDrive deleted files from backups is lower than that of data recovery without a backup. Restoring any data when the original item is deleted is expensive, plus the success of the process is not guaranteed.
Perform backups regularly
In most cases, data loss incidents happen suddenly. To recover deleted files from OneDrive with a backup, you need to ensure the viability of that backup. This can be challenging, considering the dynamics of OneDrive data changes.
Set up the frequency of your backup workflows based on the rate of OneDrive data changes in your organization. In case your employees use Onedrive intensively, weekly backups of OneDrive can be necessary to ensure smooth recoverability and production continuity.
Follow the 3-2-1 rule
The industry-accepted 3-2-1 rule serves as a template for organizing backup storage to enhance data availability through redundancy. According to this rule, you should:
- Create at least three copies of data you can’t afford to lose.
- Store those data copies on two different storage media.
- Send one copy offsite, to the cloud, or tape. For OneDrive data, which is cloud-stored by default, modern data protection solutions enable sending a copy of local backups to an offsite NAS. You can then air-gap that NAS for additional security.
Keeping up with the three points above enables you to avoid a single point of failure and have spare recovery sources in different data loss scenarios.
Configure Retention Settings
You can customize retention policies and settings in Microsoft 365. Adjusting them to your needs can help you recover OneDrive deleted files later, but you should consider the following:
- The maximum retention period you can set to store deleted items in Recycle Bin is 93 days.
- The system deletes items from Recycle Bin in case the data amount exceeds the storage quota (the default quota for OneDrive storage is 10% volume).
The limitations of the native Microsoft 365 recovery features decrease their reliability regardless of the effort and time you invest in configuration. A modern third-party Microsoft 365 backup and recovery solution can provide you with flexible retention settings and in-depth customization options. Using these capabilities, you can adjust policies and settings to your organization’s needs in terms of data retention, recoverability and regulatory compliance.
Enable versioning
With versioning enabled, you can store the pre-edited versions of OneDrive files. In case the file has unnecessary changes recorded or is corrupted, you can recover data by restoring the previous file version.
NOTE: Each file version consumes cloud storage space. Additionally, the number of versions to keep is limited. Ensure that your Microsoft 365 account has enough free space and the number of versions available is sufficient for your needs before relying on versioning for data protection.
Enhance backup security
Security is another crucial consideration when you want to enhance OneDrive data protection. Just like you shouldn’t store onsite backups inside the production environment, avoid storing OneDrive backups on OneDrive. Backup data encryption is also a must to protect data from unauthorized access both on the way to a backup repository and throughout retention.
Moreover, hackers using ransomware nowadays target backups as well as production infrastructures. Without access to backups, organizations may be more likely to pay the ransom. Enable ransomware protection for your OneDrive backups to protect them from alteration or deletion. This is how you can always have a recoverable backup even if ransomware reaches your backup repositories.
Use granular recovery
Consider installing a backup solution that has a granular recovery functionality. This allows you to recover deleted files in OneDrive without the need to restore the full backup. Therefore, you can reach tighter recovery time objectives.
Additionally, granular recovery can help maintain regulatory compliance. In case the required file is unrecoverable via native OneDrive tools and Microsoft 365 archiving also fails, up-to-date backups can provide the required data for e-discovery and other legal requests.
Conclusion
You can recover deleted files in OneDrive using native tools such as primary and second-stage Recycle Bin, local folders, and point-in-time OneDrive restoration. However, to ensure the recoverability of your OneDrive items, consider using a specialized third-party solution like NAKIVO Backup & Replication that supports workflow automation, improved security, backup immutability, flexible retention and flexible recovery options.




